What Is Crypto Arbitrage & How Can You Profit?
Crypto arbitrage is the act of earning money from price gaps on the same currency on two distinct exchanges by selling and purchasing at lower and higher prices. By selling a currency at a premium price on one exchange and buying it at a discount price on another, buyers and sellers can earn money with little risk. Even though the concept is easy, successful arbitrage transactions must be executed in a timely manner, are extensive research-based on the market, and proper risk management.
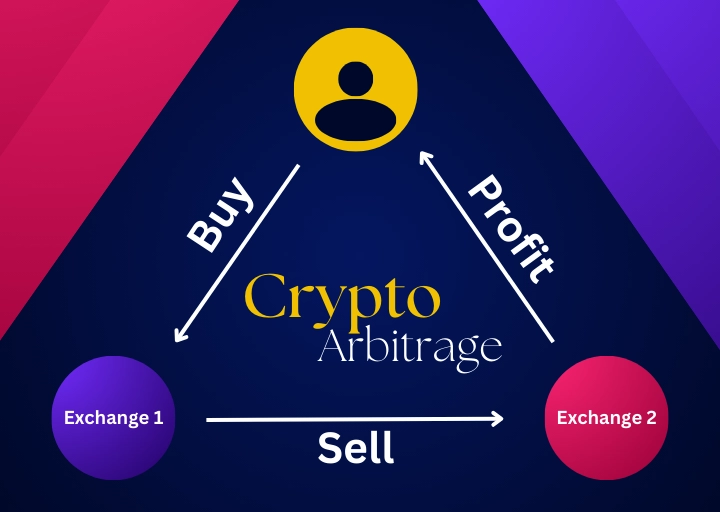
What Is Crypto Arbitrage?
Crypto arbitrage is a type of transaction where the difference in the prices of cryptocurrencies on different exchanges is exploited. Since there is no unified rate for the cryptocurrency market, every exchange is an independent operating unit, creating scope for various asset prices.
For instance, Bitcoin may be valued at $50,000 on one and $50,200 on another. One would purchase Bitcoin from the former and sell it immediately on the latter for a margin of $200.
These price changes happen for different reasons, the most common among which are differences in liquidity between exchanges. More liquid exchanges will show price movement faster than less liquid platforms. Regional demand and other fiat currencies are also causes of price changes. The decentralization of the crypto market tends to generate arbitrage spontaneously.
What Are the Main Types of Crypto Arbitrage?
Crypto arbitrage strategies may come in literally hundreds of various forms, each with a specific approach towards making money from price discrepancies among markets. The most well-known are cross-exchange arbitrage, triangular arbitrage, decentralized arbitrage, and flash loan arbitrage.
Cross-Exchange Arbitrage
It is the most basic and common type of arbitrage. It involves buying a cryptocurrency at a lower price on one exchange and then selling it at a higher price on another.
Speed is also important here, as market inefficiencies will probably be eliminated in a matter of a short time. Transfers between exchanges must also be taken into consideration by traders as this may put them out of the arbitrage window before they would be able to execute the trade.
Triangular Arbitrage
Triangular arbitrage is price discrepancies among three pairs of alternate trading within the same exchange.
For example, the trader would take note of differences in prices for Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and Litecoin (LTC). Traders make subsequent trades roll back from these vehicles to the underlying cryptocurrency in order to take advantage of the disparity to make money. Volatility of exchange rates on any one of the three vehicles creates or eliminates such opportunities for arbitrage.
Decentralized Arbitrage
This method depends on arbitrage between centralized exchanges (CEXs) and decentralized exchanges (DEXs). DEXs use automated market makers (AMMs) whose prices are determined by the mechanisms of the liquidity pool, which are automatically determined to produce price discrepancies relative to centralized exchanges using order book mechanics.
By buying an asset at one of the lower prices and selling it at the other higher price, traders can take advantage of these changes. Decentralized finance (DeFi) is particularly relevant to this strategy as it expands.
Flash Loan Arbitrage
Flash loan arbitrage is a high-level arbitrage strategy facilitated by DeFi platforms. It allows traders to borrow large sums of cryptocurrency uncollateralized, provided the loan is paid back in the same blockchain transaction.
In this, borrowed capital is utilized to take advantage of price disparities between pools of liquidity or exchanges, and the loan is paid back prior to the closure of a transaction. Smart contracts have significant dependency on flash loan arbitrage, which exposes one to DeFi mechanics as well as coding in blockchain.
How To Profit From Crypto Arbitrage
Profiting from crypto arbitrage hinges on several key factors, including timing, speed, liquidity, and transaction costs. Among these, speed is paramount. Unlike traditional financial markets, cryptocurrency trading occurs around the clock, with prices changing constantly. Traders must act swiftly to capitalize on fleeting price discrepancies.
In order to have an edge, the majority employ automated trading robots that are able to scan numerous exchanges simultaneously and make trades in seconds. Such robots are useful when employing techniques such as cross-exchange and triangular arbitrage, in which a second matters.
Another fundamental component is transaction cost management. All trades incur charges – trading, withdrawal, and blockchain network fees—and these can erode profit. Traders need sufficient spread between buying and selling prices to cover these expenses. Lower trading fees for possessors of a native token are one of the exchanges offered, offering another expense-cutting opportunity, similar to rewards earned through the utilization of crypto credit cards.
Liquidity
Liquidity is also an important consideration when executing arbitrage strategies. Liquid markets enable traders to execute large-size trades without considerably influencing the price of the asset.
Conversely, low liquidity can lead to slippage when the executed price is inferior to the rate expected. It destroys potential profit. Traders should therefore desist from it by opting for platforms that support high volumes of trading and normal liquidity, filling the trades at or near the preferred price.
What Are the Risks of Crypto Arbitrage?
Though crypto arbitrage is lucrative, it is not riskless. Understanding these risks is essential to long-term success.
Volatility
The cryptocurrency market is famously volatile. Prices can fluctuate wildly in a matter of seconds. Even brief delays in making trades can turn a potential profit into a loss. For example, the price of a token can shift while it’s being transferred between exchanges, erasing any profit margin.
Slippage
Slippage refers to the difference between the price that was expected and the real executed price of a trade. It occurs during periods of high volatility or on poorly liquid exchanges, and can considerably reduce, if not eliminate, arbitrage profits.
Exchange Withdrawal Delays
Processing delays for withdrawals from exchanges may also hinder arbitrage transactions. Processing withdrawals on some platforms is time-consuming, and heavy traffic on the blockchain network further delays transactions. For example, excessive Ethereum gas costs during heavy traffic can consume substantial profit.
Regulatory Risks
Crossing borders also has regulatory concerns. Regulations for transferring digital assets vary by nation, and traders can face fines, surcharges, or get banned if they don’t comply with local policy. Understanding the legal framework of your trade is vital in an effort to make things simple.
What To Know About Automated Tools for Crypto Arbitrage
Due to the pace of the crypto market, arbitrage traders are no longer able to manage without automation.
Bots
Trading robots are computer programs that constantly monitor prices across trading platforms and automatically trade when they spot an arbitrage opportunity. Bots can be programmed to implement particular strategies and run 24/7 without the need for regular human monitoring.
Arbitrage Calculators
These utilities help traders determine if a price difference is worth taking. By factoring in fees such as trading, transfer, and withdrawal fees, calculators provide an accurate estimate of potential profit before a trade is executed.
Alert Systems
Customized alerts notify traders of significant price differences between exchanges. Traders can set thresholds to be notified only when an opportunity is worth the given profit thresholds, allowing for timely and informed decision-making.
What Are Some Best Practices for Crypto Arbitrage Traders?
Beginners must begin with small trades so as to reduce risk while learning about arbitrage. Exchanges have to be chosen properly as well. Some exchanges offer quicker transactions, lower fees, or better liquidity.
Continuous optimization of trading strategies relative to market trend, fee, and liquidity levels will provide better results. Spread of trades among exchanges and cryptos and placing stop-loss orders are also critical to minimizing risk.
Lastly, staying up to date with crypto news and trends can allow the trader to see changes coming and adapt their strategy in real time.
The Bottom Line
Crypto arbitrage is a strategy that exploits price disparities between the decentralized and highly fragmented crypto market to make profit with comparatively low risk. Whether in cross-exchange trades, triangular schemes, or complex schemes like flash loans, arbitrage offers a unique way of making money out of market inefficiencies.
Of course, success is dependent on timely execution, accurate cost estimation, and efficient risk control. With the appropriate combination of tools, insight, and self-discipline, crypto arbitrage is a powerful way to make money in the dynamic world of digital assets.

Principal Consultant